In this era of technological evolution, the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape continues to expand, offering opportunities and innovations for businesses. In the article, we will share the latest trends and practical implementations of IoT technology in 2023. This concise guide offers a comprehensive overview of cutting-edge IoT applications, providing readers with a step-by-step roadmap to understand the transformative power of IoT in various domains.
I. Trends and Domains in the IoT Market
The IoT market is evolving as new technologies and applications emerge. By 2025, the number of Internet of Things devices connected to the Internet could reach 28 billion, assuming the current pace of technological progress.
This technology enables a global infrastructure that supports advanced services based on wireless communication technologies. It also enhances the ability to communicate and perform various tasks without human intervention. The COVID-19 pandemic has affected all social environments, such as banks, restaurants, schools, and medical centers. Those forces forced them to change their ways of operating. The IoT market has benefited from the new normality that the pandemic has created.
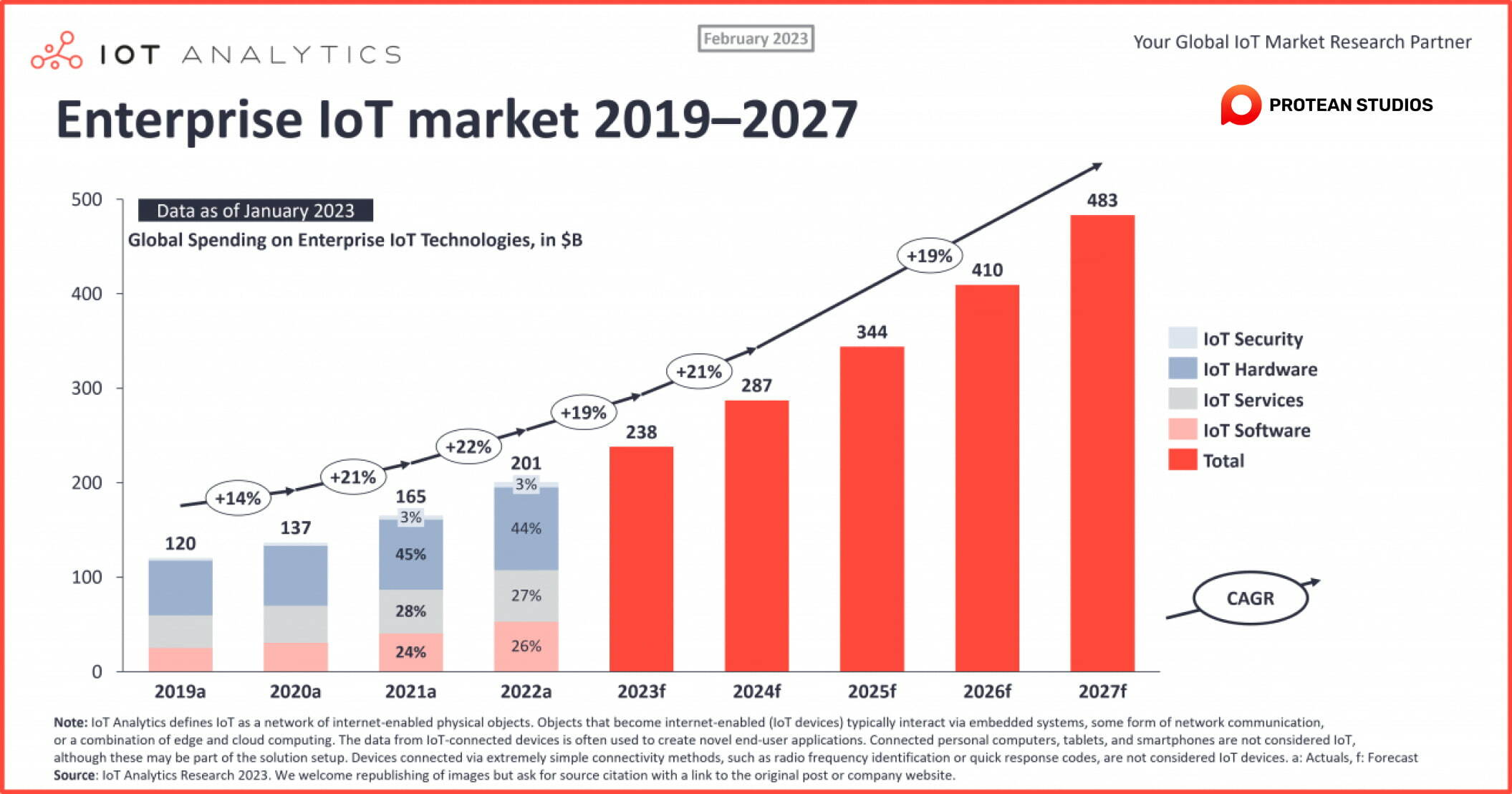
The growth of the IoT market has brought many technological advancements, such as 5G networks, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. Market research indicates that the global IoT market size will reach $1.5 trillion by 2027, and the industrial IoT sector has the largest market share. Thus, as businesses and consumers adopt IoT technology more, the IoT market growth is expected to continue soon.
II. The top 7 common IoT applications
The Internet of Things is a network of physical devices, sensors, and software that can communicate and exchange data over the Internet. IoT applications are transforming various industries and sectors by enabling new levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. Here are some of the most common IoT applications that are shaping the future of the world.
1. Transportation
IoT devices can consider traffic conditions, optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve safety for drivers and passengers. For example, smart cars can use sensors to detect obstacles, adjust speed, and alert drivers to potential hazards.
2. Smart home
IoT applications and sensors can check and control various aspects of a home, including lighting, temperature, security, and entertainment, offering a range of convenient features.
3. Manufacturing
In manufacturing, IoT ensures improved supply chain management, increased manufacturing efficiency, and monitoring and control of equipment. This helps reduce downtime and enhances effectiveness in production processes.

4. Healthcare
IoT devices can improve the delivery and quality of healthcare services because they enable remote monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment of patients. For example, wearable devices can track the vital signs, activity levels, and medication adherence of patients and send data to doctors or caregivers.
5. Retail
IoT applications in retail help enhance supply chain management, operational efficiency, and the consumer experience. They introduce features like automatic checkout, smart shelving, and targeted marketing for a more streamlined shopping experience.
6. Agriculture
IoT in agriculture optimizes the farming of animals, irrigation, and crops. This approach leads to increased food harvests, reduced manual labor, and improved efficiency in farming practices.
7. Shipping & Logistics
IoT apps also optimize the transportation and delivery of goods by enabling real-time tracking, routing, and security. For instance, smart tags can identify the location, condition, and status of packages and containers and send data to shippers or receivers.
III. How to Develop an IoT App
Developing an IoT app is a complex process that involves several steps. Here is a brief overview of how to develop an IoT app.
1. Define the requirements
The first step is to identify the problem that the IoT app will address. Then, consider the target users, the desired features and functionalities, and the business goals and metrics. This will help define the scope and specifications of the app.
2. Choose an IoT platform
An IoT platform is a software service that provides the infrastructure and tools to connect, manage, and analyze data from IoT devices. There are many IoT platforms available on the market, each with different features, pricing, and compatibility.
Some popular IoT platforms encompass AWS IoT, Google Cloud IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, and IBM Watson IoT. Choosing an IoT platform depends on factors such as scalability, security, reliability, integration, and support.
3. Choose hardware components
The hardware components of an IoT app include the sensors, actuators, microcontrollers, and communication modules. These components can collect and send data from the physical world to the cloud. The choice of hardware components depends on factors such as cost, power consumption, performance, size, and compatibility with the IoT platform and network protocol.
4. Get the network protocol
IoT devices and the cloud send and receive data according to a set of rules and standards defined by the network protocol. There are different types of network protocols for IoT, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, MQTT, and CoAP.
5. Develop the software.
The software of an IoT application consists of three layers: the firmware, the back end, and the front end.
The firmware is the software that runs on the IoT devices and controls their functionality.
The backend is the software that runs on the cloud and processes and stores data from the IoT devices.
The front end is the software that runs on the user's device and provides the user interface for interacting with the IoT app.
Thus, developing the software requires skills in programming languages, frameworks, libraries, APIs, and databases.
6. Integrate the hardware and software
The next step is to connect the hardware components with the software layers using the chosen network protocol. This involves configuring the devices, registering them on the IoT platform, establishing secure communication channels, and testing data transmission and reception.
7. Test the app
Testing the app is a crucial step to ensuring its functionality, usability, performance, security, and reliability. Developers can test apps through various methods, such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, user acceptance testing, software testing, and security testing.
8. Launch the IoT app
Once the app is ready for deployment, developers will launch it on the market. Launching an IoT app involves obtaining the necessary certifications and approvals from regulatory authorities. Then, set up a distribution channel or platform for users to download or access the app. Finally, promote and market the app to attract users and provide customer service and support.
9. Manage and control the application
The final step is to manage and track the application after its launch. This involves monitoring and analyzing data from the app to measure its performance, user behavior, feedback, and satisfaction. It also includes updating and maintaining the app to fix bugs, improve features, enhance security, and follow changing regulations.
IV. Future outlook for IoT applications in 2023
To sum up, IoT application development requires a clear strategy aligned with your business goals and user requirements. With the proper team and tools, you can create a powerful IoT app that can transform industries and enhance business efficiency.
We know that IoT is quite complicated, especially if you don’t have much experience with this kind of app. This is why our development team is ready to help you at any stage and tell you on the architecture, hardware selection, tech stack, and other aspects. If you want to know more, please contact us here.