In the era of data-driven marketing, customer data is the most valuable asset for any business. Yet, collecting, managing, and activating customer data across different channels and platforms can be challenging for them. That's where a CDP architecture comes in and supports marketers in solving these difficulties. In this blog, we will delve into customer data platforms and the way that they operate and manage data.
The trend of digital marketing with third-party data
The trend of digital marketing with third-party data is on a clear decline, with a shift towards focusing on first-party and zero-party data. There are two major factors that change this trend:
Privacy regulations: Stricter regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) are making it difficult for companies to collect and use third-party data without explicit user consent.
Deprecation of third-party cookies: Major web browsers like Chrome and Firefox are phasing out third-party cookies, which were used to track user behavior across different websites. This limits the effectiveness of using third-party data for targeted advertising.
As a result, marketers are focusing on first-party data, which is data collected from their own customers through website interactions, surveys, and loyalty programs. This data is more reliable and trustworthy, and it helps marketers know how to approach their customers.
How CDPs entered the picture of digital marketing
Customer data platforms (CDPs) are software tools that help marketers collect, unify, and activate customer data from various sources. CDPs have become popular in recent years as businesses face the challenges of data privacy regulations, third-party cookie deprecation, and rising customer expectations.

One of the main benefits of CDPs is that they enable marketers to leverage first-party data. This is the data that customers willingly share with a brand through their interactions and transactions. This data is more accurate, relevant, and trustworthy than third-party data because it is from external sources without the customer's consent or knowledge.
First-party data is not easy to collect and use. It often comes in different formats and from different systems, such as websites, mobile apps, email, CRM, social media, and more. Marketers need a way to integrate and harmonize this data, then segment and target their customers based on their preferences, behaviors, and needs.
When using the CPD architecture, it can ingest and process first-party data from many sources. Then, create a unified and comprehensive view of each customer. CDPs can also enrich this data with more attributes, such as location, device type, sale history, etc. Thus, marketers can use the data to deploy marketing strategies.
Learn more: Customer Data Platform (CDP)
CDP architecture and its features
CDP architecture takes place in five phases: tracking, matching, user profile, segmentation, and activation. The main goal is to build personalized and effective marketing strategies.
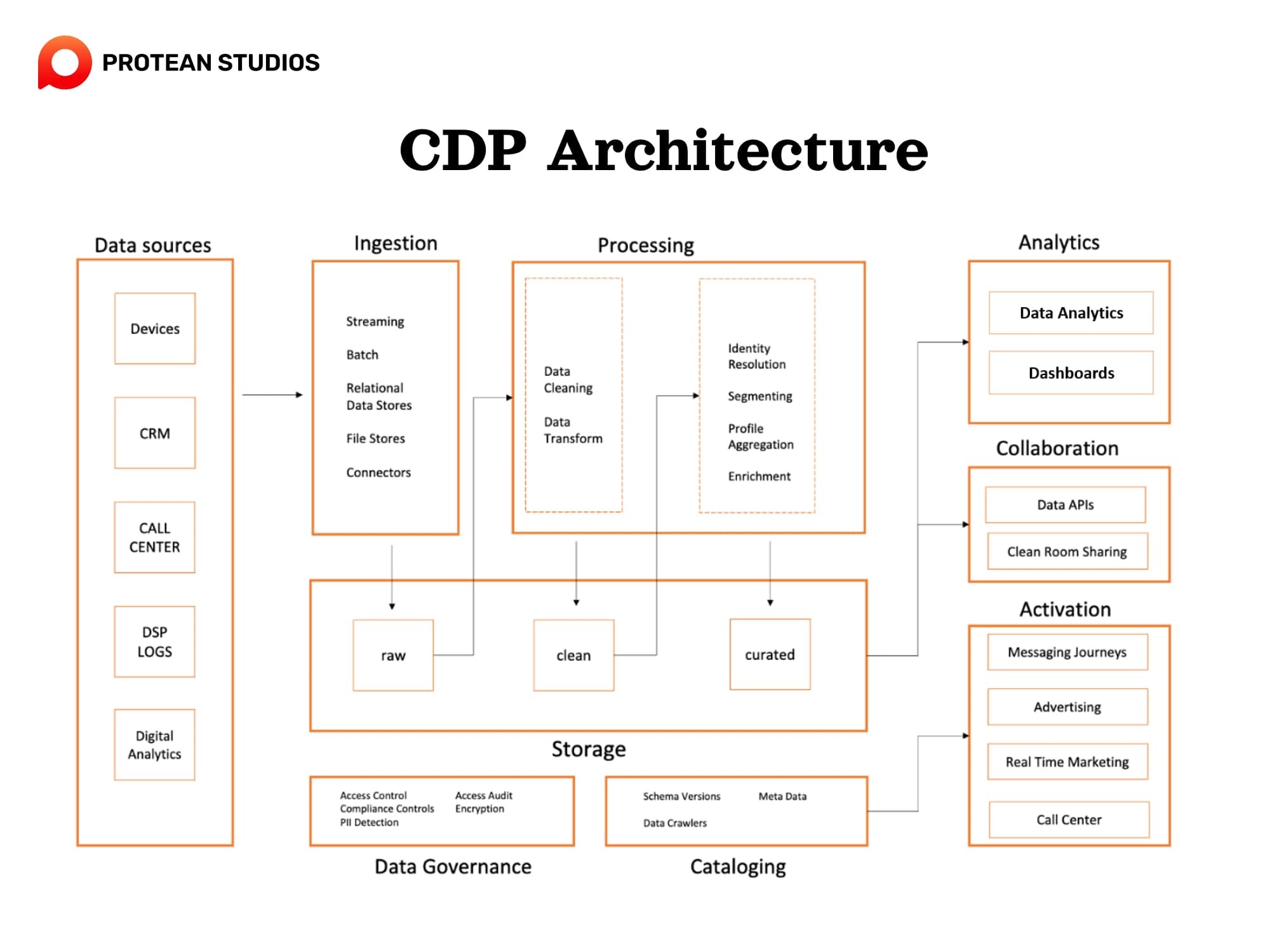
1. Event Tracking
The foundation of a CDP lies in its ability to capture customer interactions across different channels. This feature, known as event tracking, gathers data points like website visits, app usage, email opens, and sales, along with timestamps, locations, and actions taken. By capturing these micro-moments, CDPs create a detailed picture of your customer's journey, revealing their preferences and behavior patterns.
2. ID matching
ID matching is the process of linking customer identities across different platforms and devices. It enables marketers to create a single view of the customer and avoid data silos. CDP can use many platforms to match ID, such as deterministic matching (based on unique identifiers like email or phone number), probabilistic matching (based on statistical algorithms), or hybrid matching (a combination of both).
3. User Profile Storage
The CDP acts as a central repository for all customer data collected through event tracking. This user profile storage feature organizes and stores a wealth of information, including demographics, preferences, sales history, and engagement levels. By accumulating this data, the CDP builds a rich and individual profile for each customer. This is a valuable knowledge base for understanding a business's audience.
4. Segmentation
Segmentation is the process of grouping customers based on common attributes or behaviors. Segmentation allows marketers to create targeted and relevant campaigns for different segments of customers. By segmenting their audience, marketers can tailor messaging and campaigns to resonate with specific customer groups, maximizing the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Other Article: CDP Vs. CRM Vs. DMP: What's the Difference?
5. Activation
Activation is the final phase of a CDP architecture. CDPs aim to improve marketing activities by leveraging all the data available to businesses. This is the process of delivering personalized and consistent messages to customers across different channels and devices. Activation also allows marketers to increase customer engagement, loyalty, and conversion.
Transforming CDPs into marketing strategies
Digital marketing is experiencing significant innovation, striving for enhanced performance while exploring novel approaches to uphold user privacy. Today, first-party data holds the potential to impact the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
By understanding these five key features, marketers can unlock the true potential of CDPs. These platforms empower businesses to:
Gain a unified view of their customers: Break down data storage and fragmented information to truly understand customer behavior and preferences.
Deliver personalized experiences: Craft targeted marketing messages and campaigns that resonate with individual customer segments.
Optimize marketing efforts: measure the effectiveness of campaigns based on individual customer responses and refine strategies for better results.
In short, businesses should embrace customer data platforms (CDPs) to track user interactions. And then, synchronize their IDs across various channels, merge their profiles, categorize them into audiences, and activate the necessary data on marketing platforms. This is foundational to developing high-performing campaigns.