In the age of strict privacy regulations and the decline of third-party cookies, these force marketers and businesses to change into a new data landscape. In 2024, the focus is shifting towards data owned and directly collected from customers. In particular, marketers will collect data from zero-party data and first-party data resources. Below, I will share the rising trends in data collection and explore how they are shaping the future of customer insights and marketing strategies in 2024.
Types of common data
Categorize data based on how it's collected and who owns it. This understanding is crucial for businesses to navigate privacy regulations and develop effective data-driven marketing strategies. Here are some popular types of data that many companies use.
1. Zero and first-party data
Zero and first-party data are the data that a business collects directly from its own sources, such as website visitors, app users, email subscribers, or loyal customers. This type of data is the most accurate, relevant, and trustworthy, as it reflects the behavior and preferences of the target audience.
“According to McKinsey, fast-growing companies achieve a 40% increase in revenue through personalization compared to their counterparts.”
Thus, this data can help to personalize marketing campaigns, optimize the user experience, and increase customer loyalty.
2. The second-party data
Second-party data is the data that a business gets from another business that has a similar or complementary audience. For example, a travel agency might partner with a hotel chain to share their customer data and offer more relevant deals. Second-party data helps to expand the reach of marketing campaigns, find new prospects, and create strategic partnerships.
If you want to know how to manage data, you can consider these platforms via the blog: Data Management Platforms (DMPs)
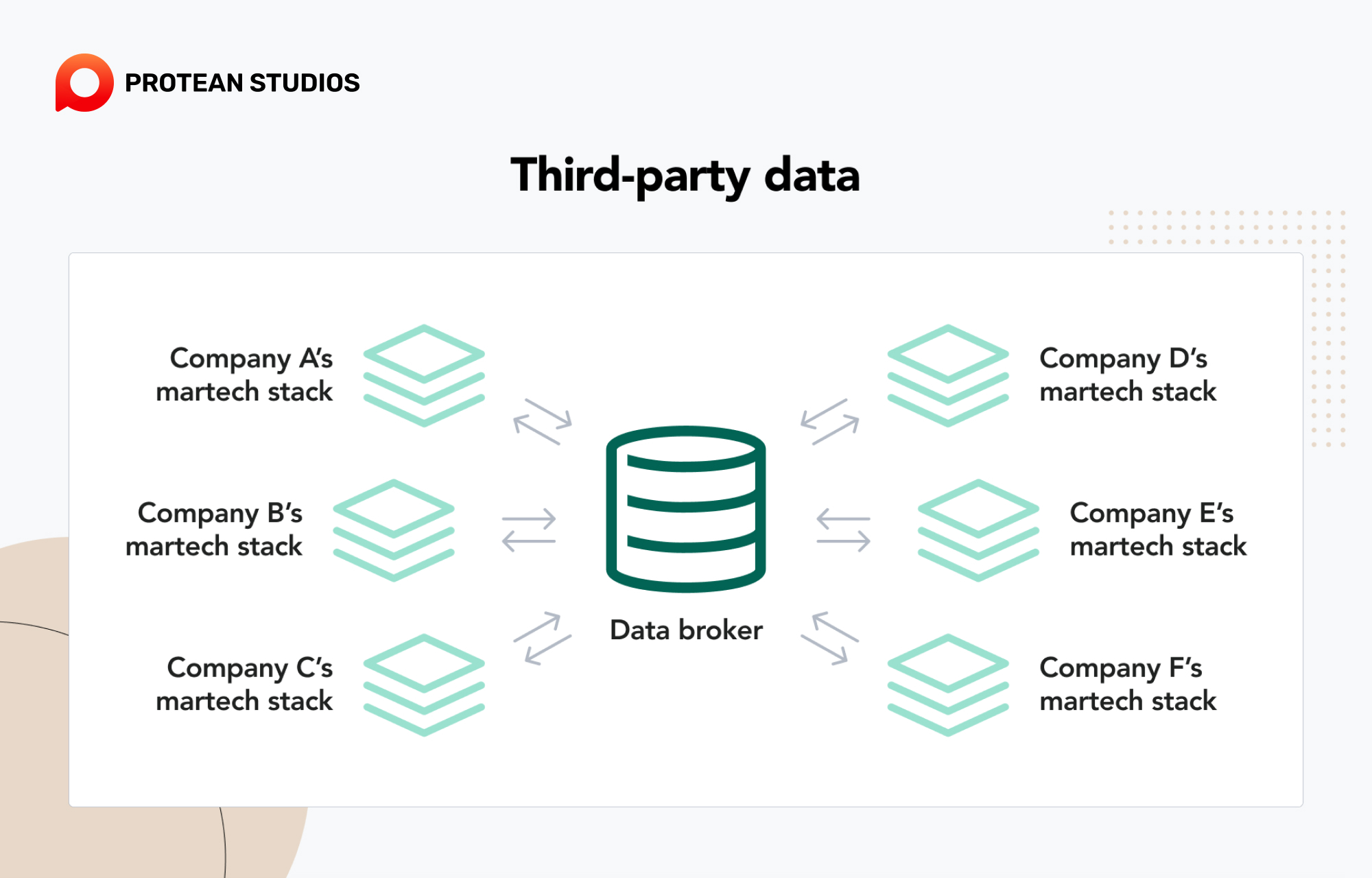
3. The third-party data
With third-party data, a business buys data from a third-party provider, such as a data broker, aggregator, or platform. This type of data is the most abundant, diverse, and accessible because it covers a wide range of topics, segments, and sources. Yet, with growing privacy regulations, the availability and reliability of third-party data are decreasing because most people don’t know their data is being collected.
As highlighted in a Wharton School article, many individuals are unaware of the extent to which their activities are being tracked. Furthermore, Elea Feit, a senior fellow at Wharton Customer Analytics and a marketing professor at Drexel, emphasizes that “most companies are now collecting data on every customer interaction as part of their regular business operations.”
According to Feit, individuals should guess that every interaction with a company results in the recording of information, which is then connected to them.
Distinguish among zero, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd party data
To help you know about the difference between zero, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd party data, you can see it in the table below.
Data Type | Description | Ownership | Example |
Zero-party data | Users provide their information. | User | Demographics, preferences, and feedback through surveys, polls, and loyalty programs. |
First-party data | Gather data through a user's interaction with your company's touchpoints. | Company | Browsing behavior, sales history, and engagement metrics on your website or app. |
Second-party data | Non-anonymized first-party data from a partner company with overlapping audiences. | Shared between companies | An airline accessing frequent flyer data from a travel agency (with user consent). |
Third-party data | Collecting data by aggregators from various sources, including public records and websites. | Data provider | Companies buy demographic, behavioral, or interest-based data from a data supplier. |
Deeper insights: CDP vs. CRM vs. DMP: What's the Difference?
Why is 2024 the era of zero-party data and first-party data?

2024 presents a unique opportunity for companies to shift their focus from external data sources to building stronger relationships with their customers. There are several reasons why 2024 is shaping up to be the era of zero-party and first-party data:
Privacy Regulations: Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) are giving users more control over their data. This makes it harder for companies to rely on third-party data sources that might not follow user consent requirements.
Decline of Third-party Cookies: Third-party cookies, once a mainstay for online tracking, are being phased out by major browsers due to privacy concerns. This reduces the effectiveness of traditional methods of gathering user data across different websites.
Building Trust: Consumers are wary of how their data is collected and used. By focusing on zero-party and first-party data, companies can build trust by being transparent about data collection practices and getting explicit user consent.
Increased Personalization: Take advantage of zero-party and first-party data, which allows for hyper-personalization of marketing campaigns, product recommendations, and customer experiences.
Guidelines to use zero and first-party data for personalized marketing?
The rise of zero-party and first-party data presents a golden opportunity for personalized marketing. To use this data, you need to follow some hints below.
1. Transparency and consent
Share how you collect and use data.
Explain the benefits of personalization to users and get their explicit consent.
Make it easy for users to access, update, or delete their data.
2. Collect high-quality zero data
Design engaging surveys, polls, and quizzes to gather valuable user preferences and interests.
Offer incentives for participation, but ensure rewards don't skew the data.
Run interactive contests or loyalty programs to encourage data sharing in a fun way.
3. Leverage user behavior from first-party data
Analyze website and app behavior to understand user journeys and preferences.
Track sales history and product interactions to identify buying patterns.
Use website heatmaps and clickstream data to personalize product recommendations.
4. Segment your audience
Combine zero-party data with first-party data to create detailed customer segments.
Group users based on demographics, interests, sales history, and website behavior.
Tailor marketing messages and offerings to resonate with each specific segment.
5. Personalize the customer’s experience
Use first-party data to personalize website content, product recommendations, and email campaigns.
Deliver targeted ads based on user interests and browsing behavior.
Create dynamic landing pages with personalized offers based on user data.
Summarize data trends
In summary, the rise of first-party and zero-party data shows a new era of personalization. As companies adapt to these trends, they position themselves to collect data and create meaningful customer experiences. You need to remember that data isn’t just a commodity—it’s the heartbeat of informed decision-making and customer-centric strategies.





